File Formats¶
This page describes the output file formats produced by megalodon.
Base Calling¶
Basecalling produces either FASTQ or FASTA formats.
Basecalls will be output into the basecalls.fastq or basecalls.fasta file within the --output-directory.
As of version 2.2, basecall anchored modified base calls (mod_basecalls) are output in an unmapped BAM file via the Mm and Ml tags described by hts-specs here..
Mapping¶
Mapped reads can be output in SAM, BAM or CRAM formats.
Basecalls will be output into the mappings.sam, mappings.bam, or mappings.cram file within the --output-directory.
Mapping Summary¶
When --outputs mappings is requested the mappings.summary.txt is produced.
This file contains the following fields:
read_id
Unique read identifier (from FAST5)
pct_identity
Mapping/reference percent identity (computed as
100 * num_match / num_align)
num_align
Length of full alignment (
num_match + num_mismatch + num_ins + num_del)
num_match
Number of basecalls aligned to a matching reference base
num_del
Number of deleted reference bases implied by the alignment
num_ins
Number of inserted reference bases implied by the alignment
read_pct_coverage
Percentage of read basecalls included in reference alignment
chrom
Reference contig name for mapping
strand
Strand for mapping
start
Reference coordinate for start of mapping (0-based close interval coordinate)
end
Reference coordinate for end of mapping (0-based open interval coordinate)
query_start
Basecall coordinate for start of mapping (0-based closed interval coordinate)
query_end
Basecall coordinate for end of mapping (0-based open interval coordinate)
map_sig_start
Raw signal coordinate for start of mapping (0-based closed interval coordinate). Note that this coordinate is as stored in the FAST5 file, so for RNA reads (5’ to 3’ read direction) the start coordinate will be greater than the end coordinate.
map_sig_end
Raw signal coordinate for end of mapping (0-based open interval coordinate)
sig_len
Length of signal for complete read
map_num
Mapping number to distinguish multiple mappings from the same read. Should always be
0when--allow-supplementary-alignmentsis not set.
Modified Base Mapping¶
As of version 2.2, the default output for the mod_mappings output type will be a single BAM file with modified base probabilities stored via the Mm and Ml tags, as in mod_basecalls above.
This format can be output in SAM, BAM or CRAM format as specified by the --mappings-format argument (which also applies to the mappings and mod_basecalls outputs).
In order to obtain mod_mappings in the same format as Meglodon version < 2.2 use the --mod-map-emulate-bisulfite flag.
This option will output a file for each modified base represented in the basecalling model.
The mapped reads in this output represent only the information about modified bases contained within each read.
Each read includes the mapped reference bases with only the called modified bases annotated.
The quality score for each called base (whether called as modified or canonical) represent the probability of a modified status and not the canonical base probability (as specified by the SAM format).
Bases without a proposed modified base will contain a quality score of 40.
In addition, the --mod-map-base-conv is provided to modulate the bases output by this format.
This option is useful since the BAM and CRAM formats do not support modified bases and will convert all alternative bases to N for storage.
For example, to mimic bisulfite output use --mod-map-base-conv C T --mod-map-base-conv Z C
This can then be visualized by a genome browser as with standard bisulfite data.
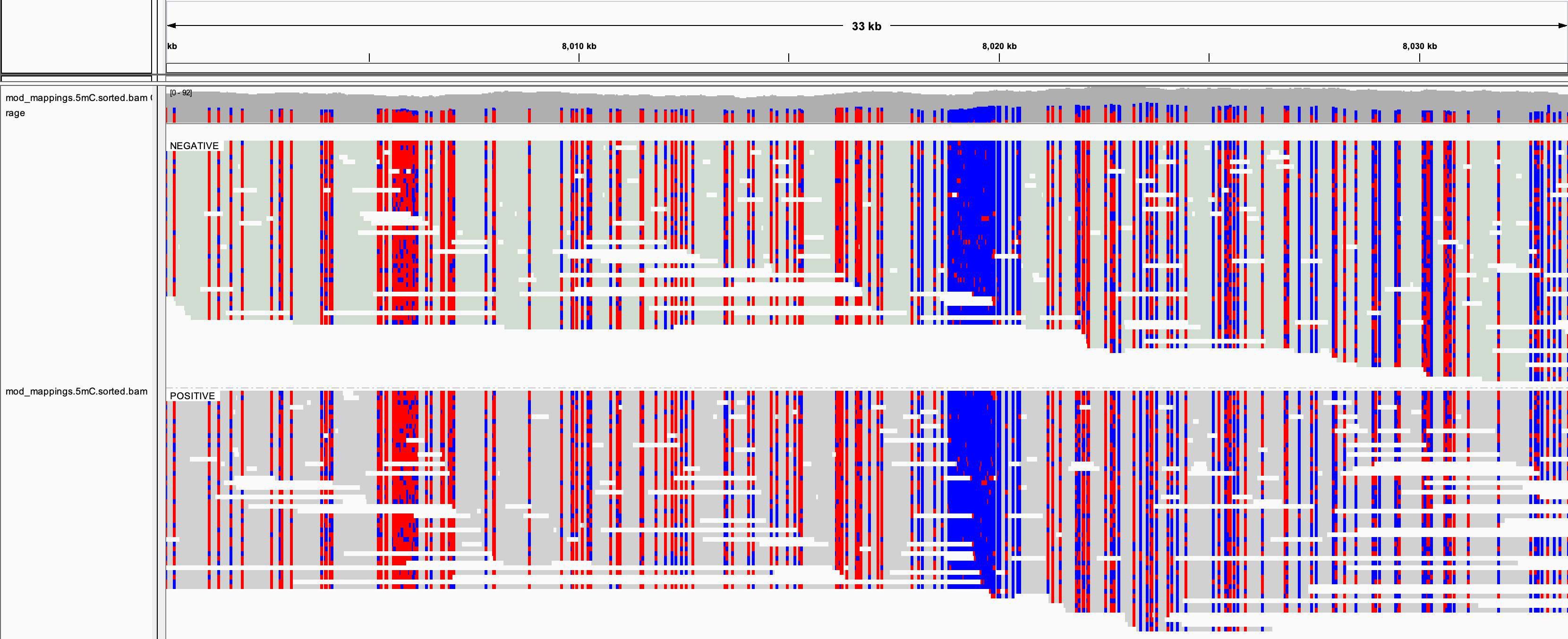
Genome browser visualization. Megalodon mod_mappings output.¶
Variant Mapping¶
In addition to standard mapping files, megalodon includes a special mapping-style output with specific relevance to the variant calling pipeline.
This format can be output as a SAM, BAM or CRAM file as with standard mapping format (as specified by the --mappings-format argument).
The mapped reads in this output represent only the information about proposed variants contained within each read.
Each read includes the mapped reference bases with only the called variants annotated.
The score for each call is encoded in the base quality scores for each read.
Bases without a proposed variant will contain a quality score of 40.
Note that storage of insertion probabilities is not supported by the SAM/BAM format, so these score are lost in this format.
This output is useful for 1) producing more accurate variant phasing and read haplotagging via whatshap and 2) visualizing per-read variant calls in a genome browser.
Per-read Modified Bases¶
Database¶
The primary output for per-read modified base results is an sqlite database.
This database contains an indexed table with per-read, per-position, modified base scores, as well as auxiliary tables with read, modification type and reference chromosomes/records information.
The read table (read) contains the read UUID.
The modification type table (mod) contains the single letter modified base code, the modified base long name and the associated canonical base.
As of version 2.2, the pos table has been dropped from the modified base schema.
In place of the pos table, the chrm table contains the name and length of each chromosome/record in the reference sequence.
The score_pos in the data table then contains an integer encoding of the (chrm, pos, strand) tuple (see megalodon.mods.ModsDb.get_pos_dbid and megalodon.mods.ModsDb.get_pos functions).
This allows more efficient access to position information without requiring additional interaction with the database.
The data table then contains the links between these tables along with the per-read log probability for each modified base at each called reference position in the score column.
This table is indexed at the end of the run by the score_pos field such that iteration over the table (via megalodon.mods.ModsDb.iter_pos_scores occurs in reference sorted order.
This database may be accessed via the megalodon.mods.ModsDb object.
More documentation on the usage of the megalodon.mods.ModsDb interface will be added in a future release.
Tab-delimited¶
Modified bases results are also available via tab-delimited text output.
This output can be requested via the --write-mods-text flag or obtained after a run via the megalodon_extras per_read_text modified_bases command.
This output contains the following fields: read_id, chrm, strand, pos, mod_log_prob, can_log_prob, and mod_base
Aggregated Modified Bases¶
The default aggregated modified base output is the bedMethyl format (description here). Alternative formats are wiggle (variableStep) and VCF (treating the modified base as if it were a sequence variant).
Per-read Sequence Variants¶
As with the modified base results, the primary output for per-read sequence variant results is as sqlite database. This database contains an indexed table with per-read, per-position, variant scores, as well as auxiliary tables with read, reference location and alternative allele information.
The reference location table (loc) contains the mapped 0-based position, strand (1=forward, -1=reverse) and chromosome (via a final chrm table which contains the chromosome text).
The loc table also contains the location for the start and end of the tested positions (applicable for insertions/deletions).
For example, insertions generally require a context base for downstream processing, but within megalodon only the inserted position is considered (without context).
Each reference location is linked to the IDs linked with this location from the input variants file.
Finally the reference sequence for the location is included in this table.
In the related alt table, each alternative sequence is stored.
Links between alternative sequences and reference locations are made via the main data table.
The read table contains the read UUID as well as the mapped strand for each read.
Aggregated Sequence Variants¶
Sequence variant calls are output in standard VCF format (version 4.1).
The sample format fields includes the following standard VCF fields: gt, gq, gp, gl, and ``pl
In addition the non-standard log_probs field, containing the per-read contributions to the variant call, can be added to the VCF file by setting the --write-vcf-log-probs flag.